I already created some content on EventBridge like for example the ones on EventBridge Pipes and EventBridge Scheduler but I got some requests to introduce EventBridge properly as many people don’t have experience with it and don’t know how to do some basic setups with it.
I won’t go into too much details on what EventBridge is as you can find the definitions on it’s website. Let’s just say that EventBridge is a serverless service that allows you to use events to connect different application components together. This way you are able to build scalable event-driven applications. It will route events from one source to another. The sources can be AWS services, your own application or third- party software.
It has many features which allow you to create schedules, pipes, create event archives and replay the events, you can set up schema discovery and then it can provide you with code bindings so you can have strongly typed events in your application.
An example EventBridge use case
Now in this article and the associated video I will show you how to set up some basic integrations for an order processing backend for a webshop. You will have:
- This article which guides you on how to set this up from the AWS Management Console
- The walkthrough in video format. Skip to the video
- A fully working AWS SAM template which you can use if you want to deploy the whole architecture in an automated manner. Skip to the SAM Template
But first let’s see what we’re building. It will be a small stack that will have the following:
- A custom event bus – this will receive the orders in the form of events
- Some rules that will determine which targets will receive our events:
- CloudWatch events rule – will forward ALL events to a CloudWatch log group for analysis
- Lambda function rule – will forward our order event to a processing Lambda function (in a real world situation this should process the order)
- Step Functions rule – will forward our order event to a state machine which will to the shipment handling and confirm once shipment of the order was completed
- An API Gateway – this will receive the orders from our webshop (we will not implement the webshop) and sends them to EventBridge
Now keep in mind that the Lambda functions that should process the order and the shipment are just skeletons, they won’t actually do any processing or shipping. They are there just as examples. Also the shipment processing state machine contains just one Lambda function, in a real world situation this would have many more steps but for the sake of simplicity I’ve done it in this simple way.
Here is the diagram of what we’re trying to build:
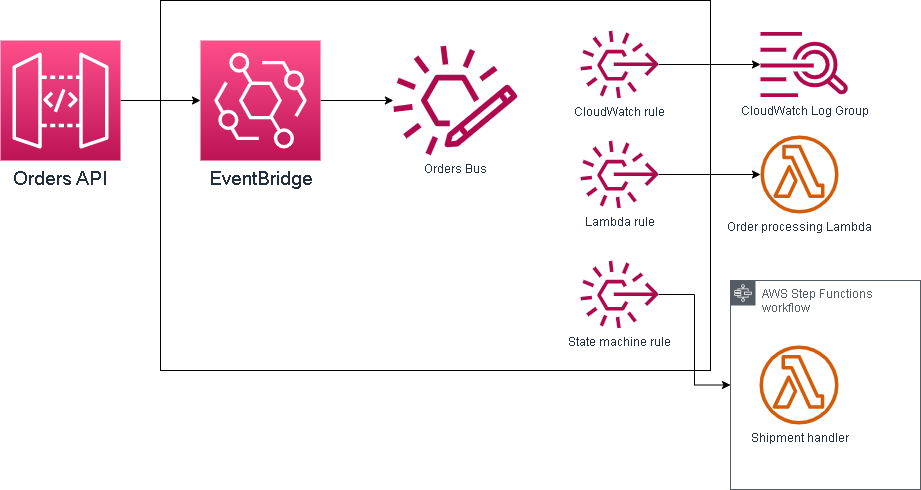
Implementation
1. Create Event Bus
First we will create the Event Bus, we will need the ARN of this event bus later
- Go to the AWS Management Console and find EventBridge. You can find it in the Services menu under Application Integration
- In the left side menu click on “Event buses” then click the orange “Create event bus” button
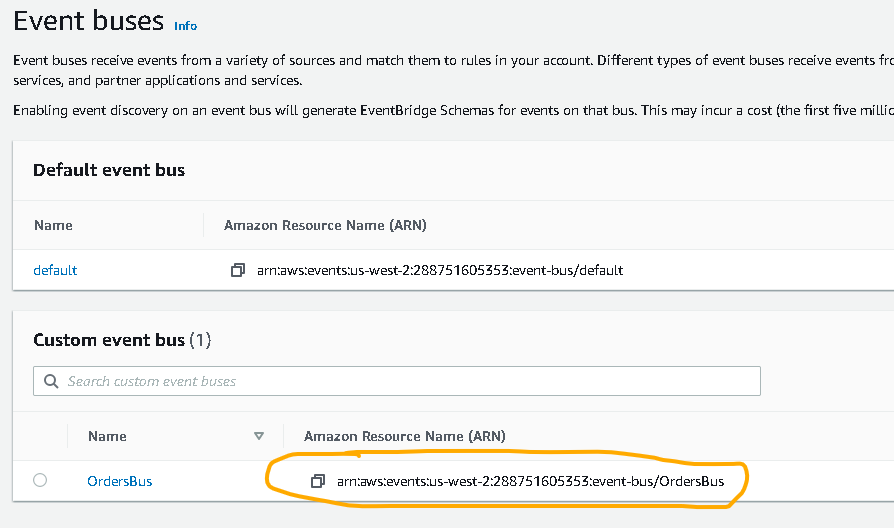
- Give your event bus a name, an example could be: “OrdersBus” then click “Create“
- In the resulting list find the ARN of the event bus (see picture below) and save it, you will need it later
2. Setting up the EventBridge rules
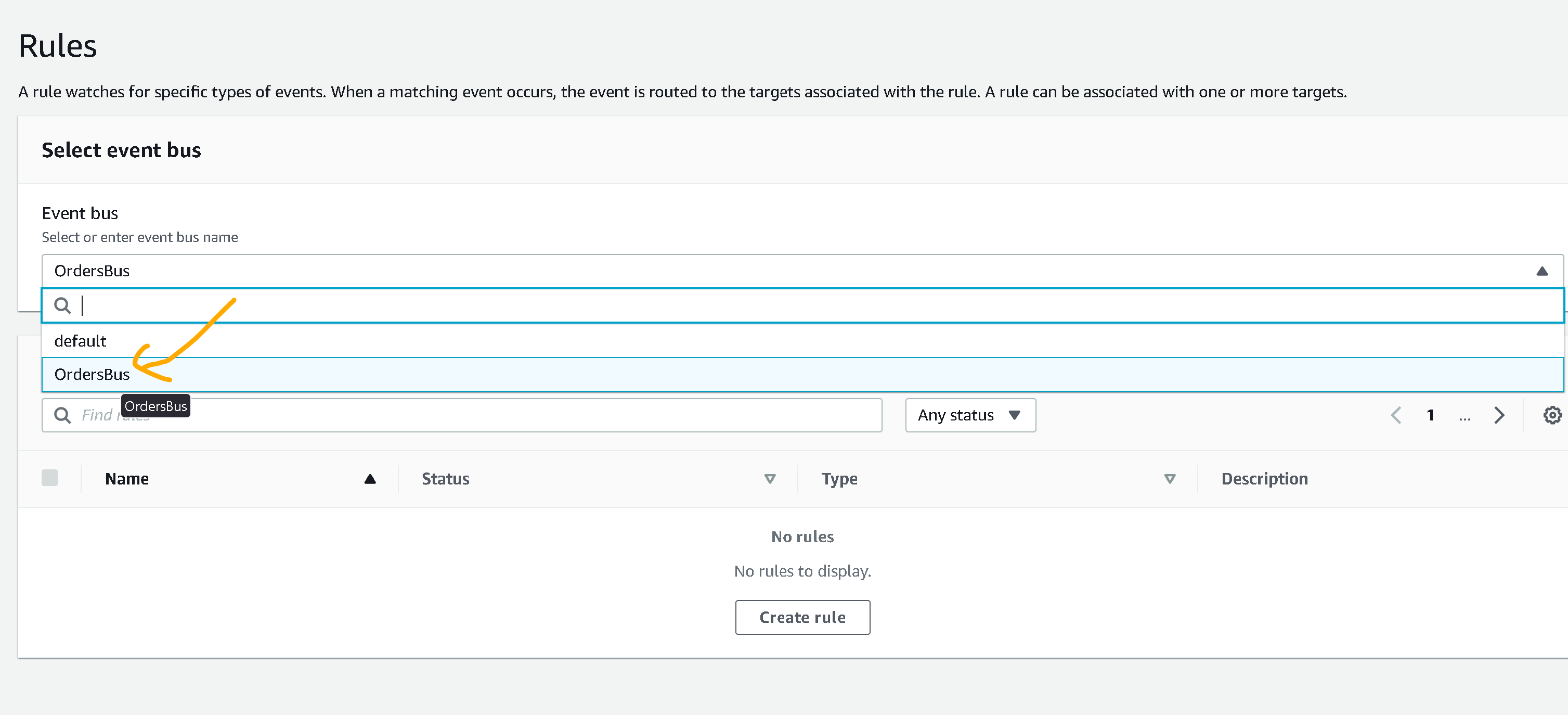
- Go to EventBridge and on the left side menu click on “Rules” then select the event bus that you have created at Step 1
CloudWatch rule
- Click on “Create rule” and then give it a name, example: “OrderToCloudWatchLogGroup“
- Click on “Next“
- For event source select “Other“
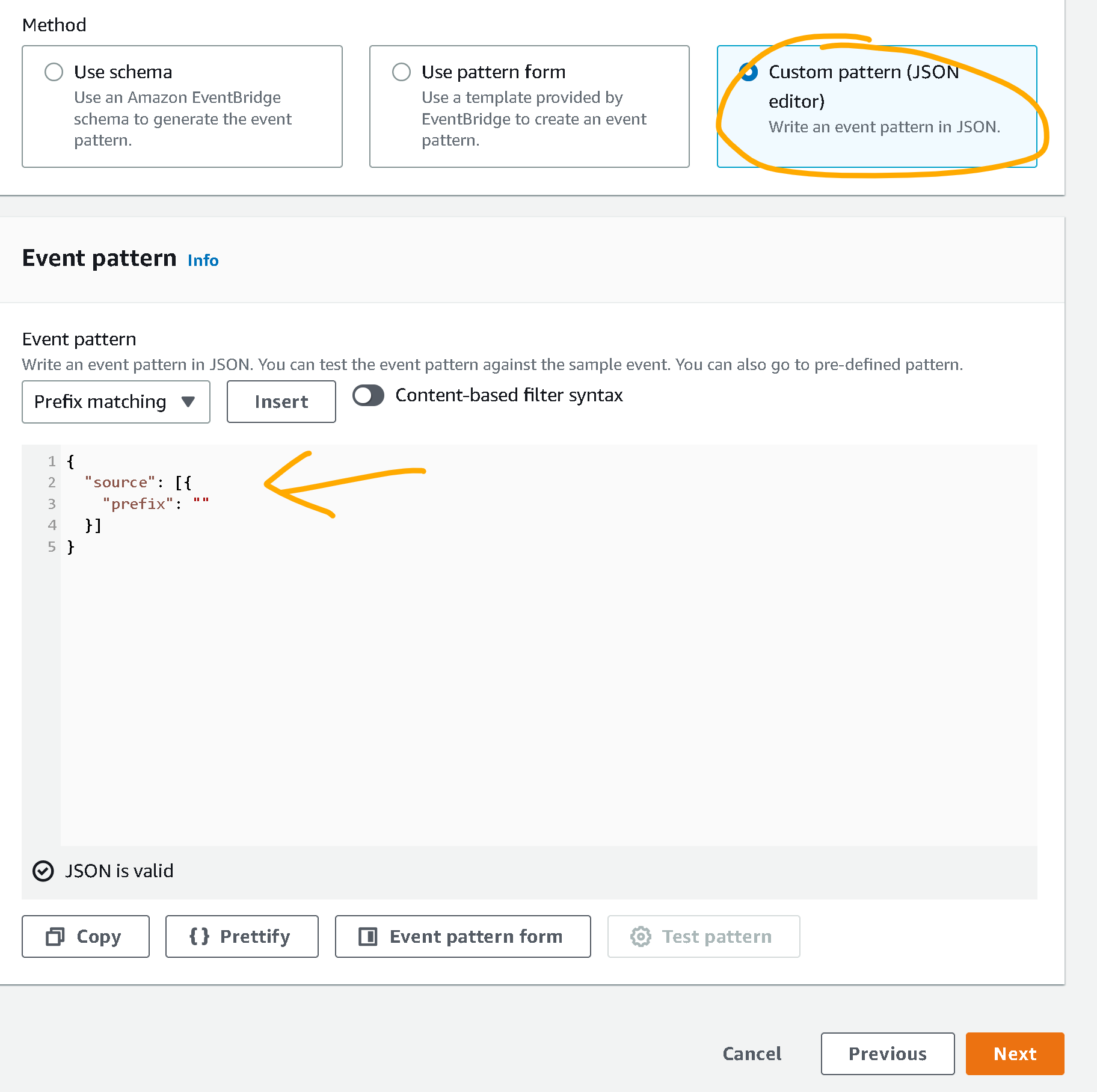
- Scroll down to “Creation method” and make sure “Custom pattern (JSON editor)” is selected
- For “Event pattern” enter the following:
{
"source": [{
"prefix": ""
}]
}This will tell EventBridge to send all events with prefix “” to the target. In this case this means ALL events will be sent to that target CloudWatch log group. We can use this for debugging.
Your setup should look like this:
- Click on “Next“
- For Target 1 choose “AWS service”
- Then at “Select a target” choose “CloudWatch log group”
- For log group, after “/aws/events/” add your own log group name, for example: “OrderEventLog” and then click “Next” then “Next” again and finally click “Create rule“
Lambda rule
Repeat the creation process for the Lambda rule, which is similar except:
- for the “Event Pattern” use the following one:
{
"source": [{
"prefix": "com.majestic.orders"
}]
}This will tell EvenBridge to only send events that have the prefix “com.majestic.orders” in the “source” property to the target.
- instead of CloudWatch log group you should choose a Lambda function that will get the event from the event bus and process it. In the SAM template below this is implemented. In this case we will skip the detailed instructions on how to create it to keep the article length manageable.
Step Functions state machine rule
Repeat the creation process for the Step Functions state machine rule, which is similar except:
- for the “Event Pattern” use the following one:
{
"source": [{
"prefix": "com.majestic.orders"
}]
}This will tell EvenBridge to only send events that have the prefix “com.majestic.orders” in the “source” property to the target.
- instead of CloudWatch log group you should choose a Step Functions state machine that will get the event from the event bus and execute a workflow for it. In the SAM template below this is implemented. In this case we will skip the detailed instructions on how to create it to keep the article length manageable. The state machine then will execute the workflow that is configured in it. You can set up a basic state machine as a target.
3. Create an IAM policy
Then we need to create an IAM policy and then a Role, this will define the permissions, we are going to need this for our API Gateway to be able to put events into the event bus
- In the AWS Management Console find the IAM service (Services menu -> Security, Identity & Compliance -> IAM)
- In the left side menu go to Policies and then click on “Create Policy“
- Switch to the JSON tab
- Add the following policy and make sure you replace EVENT_BUS_ARN with the ARN of your EventBridge event bus (what you copied above when you created the event bus)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "events:PutEvents",
"Resource": "EVENT_BUS_ARN"
}
]
}- Click on “Next: Tags” and then “Next: Review”
- Give the policy a name, for example: MyAPIGatewayEventBusPermissionPolicy and then click on “Create policy“
4. Create an IAM role
- In the IAM console click on Roles and then on “Create role“
- For Trusted Entity Type choose API Gateway from the dropdown called “Use cases for other AWS services” (just like in the screenshot below)
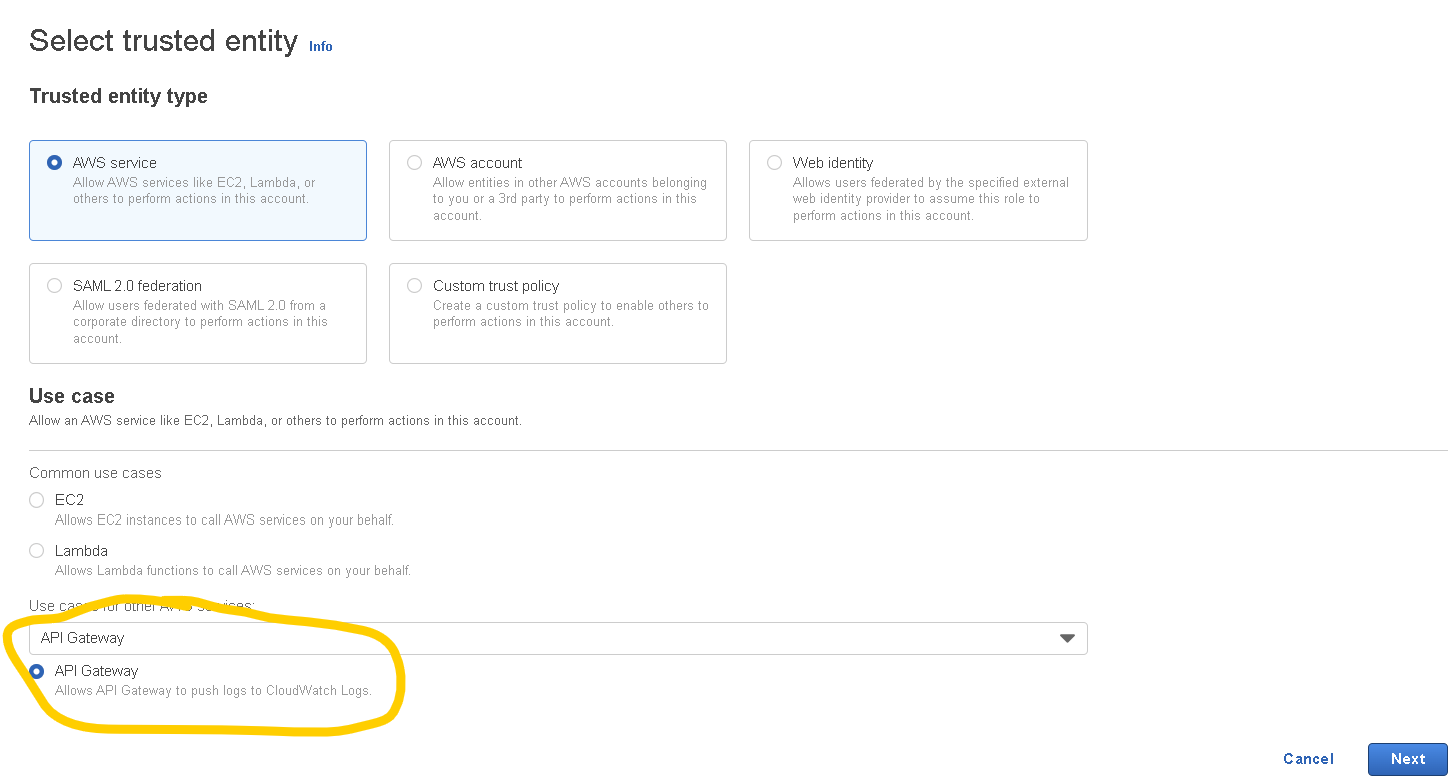
Click on “Next” then “Next” again, give the role a name (this can be anything you want) then click on “Create role“
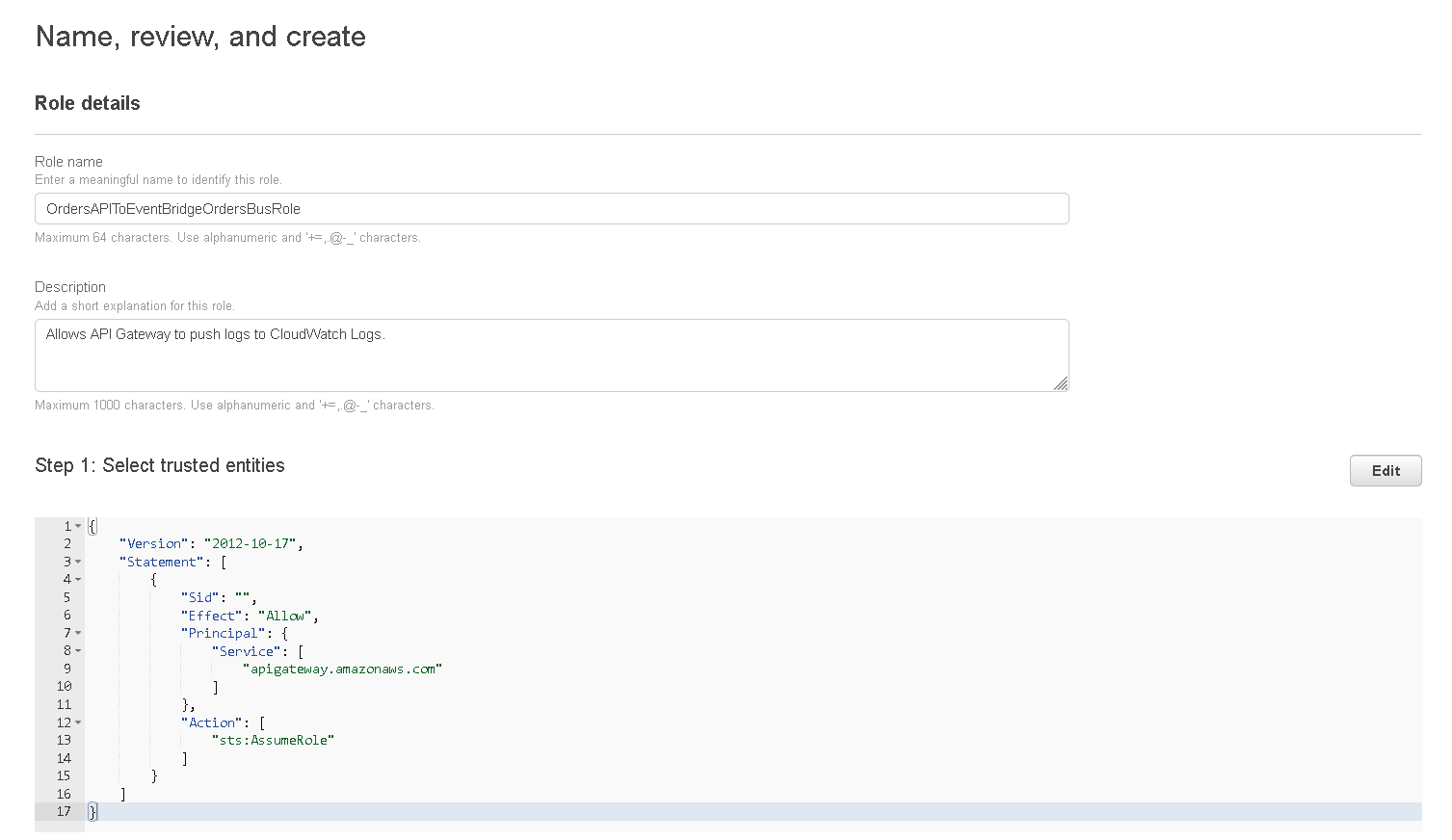
- The role will be saved but you need to open it again, find it in the list, click on the name
- When the page is loaded with the role details click on “Add permissions” and choose “Attach policies” from the dropdown.
- Find the policy you created previously (Step 3) and select it then click on “Attach policies” and then copy the “ARN” of the role, you will need this later.
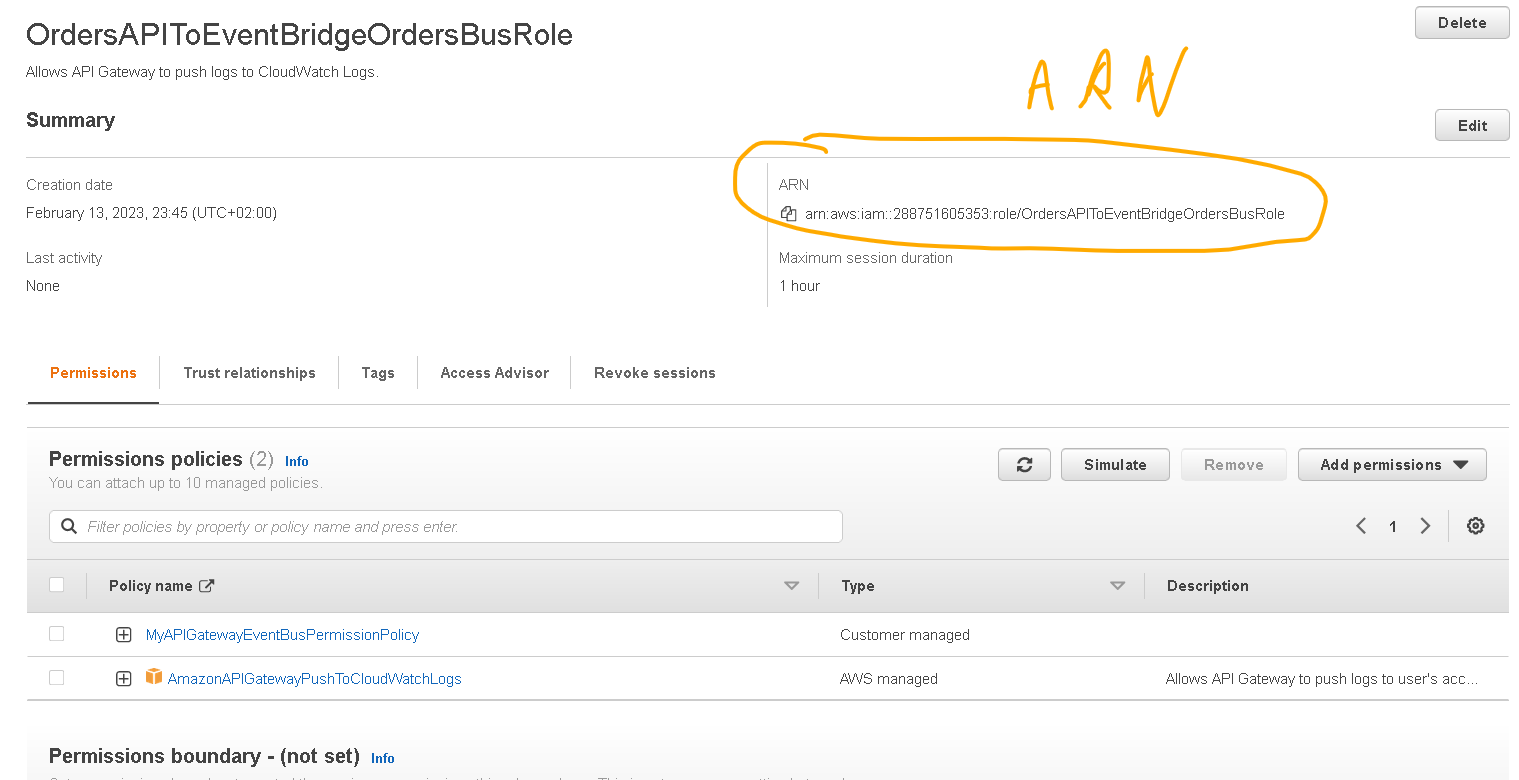
5. Create API Gateway and configure it
- Go to the API Gateway service (Services menu -> Networking & Content Delivery -> API Gateway)
- Click on “Create API” and then on the “REST API” choose “Build” (make sure you don’t choose REST API Private)
- On the next page make sure you have “REST” selected and “New API” selected, then give your API a name then click on “Create API“
- On the API page open the “Actions” dropdown select “Create Resource” and give a name to your resource, for example: “orders” then click on “Create Resource“
- Click on the resource that you just created then on the “Actions” menu again and select “Create Method“.
- On the created method select “POST” and then click on the checkmark.
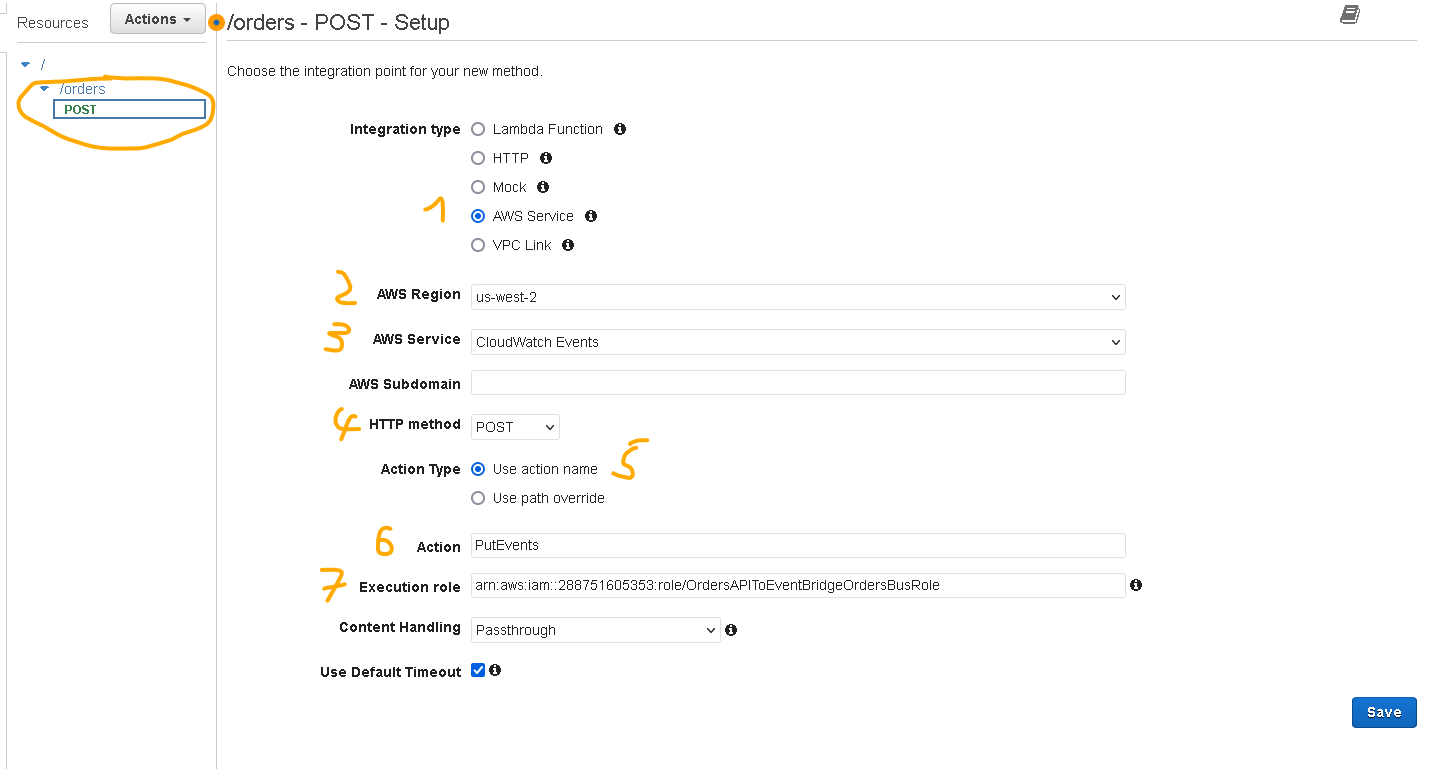
- You will see the integration page where you need to setup some additional stuff (refer to the screenshot below (numbers match screenshot numbers).
- 1. For integration type select “AWS Service”
- 2. For the AWS region select your preferred region
- 3. For AWS Service select “CloudWatch Events“
- 4. For HTTP method select “POST“
- 5. For Action Type select “Use action name“
- 6. For Action type PutEvents
- 7. For the Execution role paste in the ARN of the Role that you created at step 4 and then click “Save“
On the page that is shown select “Integration Request”
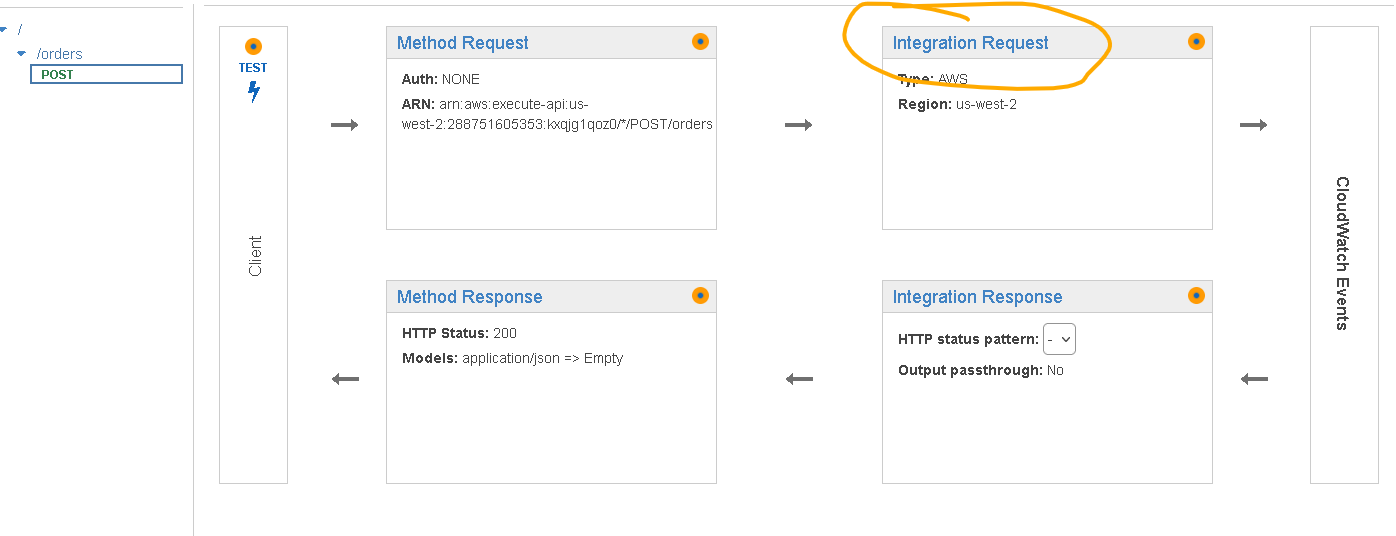
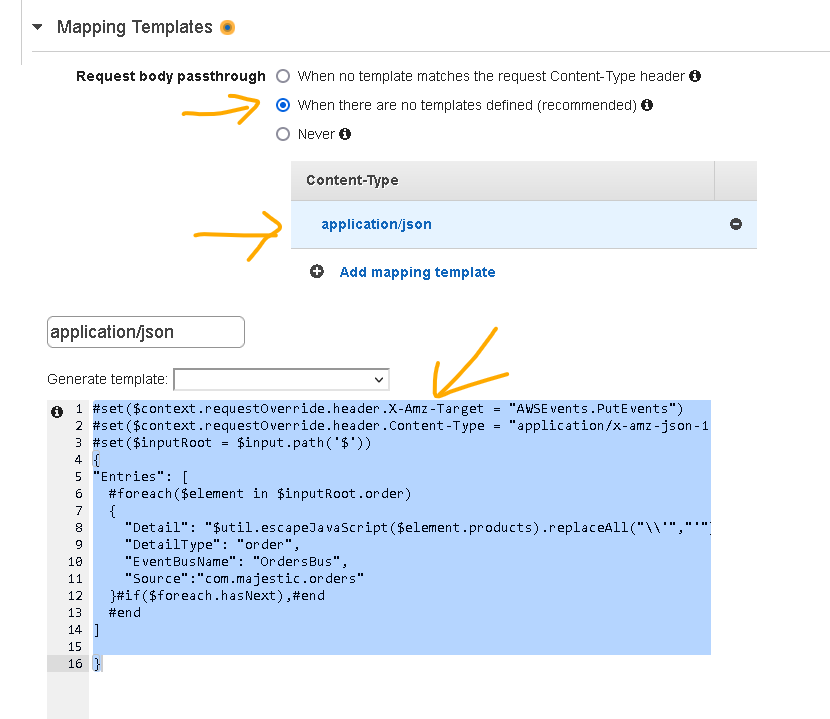
- Scroll down to Mapping Templates and expand that section
- For the Request body passthrough, select the option that fits your needs
- Choose Add mapping template and then for Content-Type, enter application/json and choose “Create“.
- For the template, enter the following
#set($context.requestOverride.header.X-Amz-Target = "AWSEvents.PutEvents")
#set($context.requestOverride.header.Content-Type = "application/x-amz-json-1.1")
#set($inputRoot = $input.path('$'))
{
"Entries": [
#foreach($element in $inputRoot.order)
{
"Detail": "$util.escapeJavaScript($element.products).replaceAll("\\'","'")",
"DetailType": "order",
"EventBusName": "OrdersBus",
"Source":"com.majestic.orders"
}#if($foreach.hasNext),#end
#end
]
}
- Make sure the “EventBusName” above is set to your event bus name (what you have created at Step 1)
- Click on “Save“
6. Deploy the API and send some test orders to the POST method
- While still on the API page click on the “Actions” dropdown and select “Deploy API” then in the Deployment stage dropdown select [New Stage] , give it a name, example: prod and then click “Deploy“
- Test the integration with curl from the command line, make sure to replace the following:
- API_ID with the ID of your API (you can find this in the API Gateway console, go to the list of your API Gateways and in the list there is also the ID besides the name)
- REGION with your preferred region id, for example us-east-1
- STAGE with the stage you created earlier (I used prod above)
- RESOURCE with the name of your resource (route), I used orders above.
- For the payload section we are adding the orders, look at my example below, under the order property I actually have to products that are being ordered. Each of these will generate a separate event in the event bus, so you should have 2 EventBridge events fired
curl --location --request POST 'https://API_ID.execute-api.REGION.amazonaws.com/STAGE/RESOURCE' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"order":[
{
"products":"{\"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"chair\"}",
},
{
"products":"{\"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"sofa\"}",
}
]
}'- You should be getting back something like this:
{"Entries":[{"EventId":"13bbb491-6444-6312-d3c0-efbccb058fdf"},{"EventId":"a347c3e3-5dd4-b7a8-0534-e364a1c9a1fe"}],"FailedEntryCount":0}- So that’s about it. Now you should have a working integration between API Gateway and EventBridge and your incoming orders will be sent to EventBridge from where you will be able to process them in an asynchronous manner with the configured targets.
7. Verifying events in your targets
- If you want to see that your events were successfully received by your targets you can go to CloudWatch logs and check the appropriate log groups:
- For your configured CloudWatch rule group
- For the processore Lambda function
- For the Step Functions state machine
8. SAM Template
If you just want to deploy this whole thing in an automated way then here’s the SAM template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Resources:
# This is the API Gateway that will receive the orders to it's endpoint
OrdersAPI:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
EndpointConfiguration:
Type: REGIONAL
StageName: Prod
DefinitionBody:
swagger: "2.0"
info:
title: OrdersAPI
paths:
/orders:
post:
consumes:
- "application/json"
produces:
- "application/json"
responses:
"200":
description: "200 response"
schema:
$ref: "#/definitions/Empty"
x-amazon-apigateway-integration:
type: aws
uri: !Sub "arn:aws:apigateway:${AWS::Region}:events:action/PutEvents"
credentials: !GetAtt "APIGatewayExecutionRole.Arn"
httpMethod: "POST"
responses:
default:
statusCode: "200"
requestTemplates:
application/json: !Sub
- |-
#set($context.requestOverride.header.X-Amz-Target = "AWSEvents.PutEvents")
#set($context.requestOverride.header.Content-Type = "application/x-amz-json-1.1")
#set($inputRoot = $input.path('$'))
{
"Entries": [
#foreach($element in $inputRoot.order)
{
"Detail": "$util.escapeJavaScript($element.products).replaceAll("\\'","'")",
"DetailType": "order",
"EventBusName": "${EventBusName}",
"Source":"com.majestic.orders"
}#if($foreach.hasNext),#end
#end
]
}
- { EventBusName: !Ref OrderEventsBus }
passthroughBehavior: "when_no_templates"
# This is the API Gateway Execution Role
APIGatewayExecutionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Principal:
Service:
- apigateway.amazonaws.com
Policies:
- PolicyName: APIGatewayEventBridgePolicy
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- events:PutEvents
Resource: !Sub "arn:aws:events:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:event-bus/OrderEventsBus"
# This is our EventBus
OrderEventsBus:
Type: AWS::Events::EventBus
Properties:
Name: OrderEventsBus
# Lambda Function that has an event rule attached. It will get an event every time the pattern is matched
ProcessorLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: src/
Handler: orderProcessor.processOrder
Runtime: nodejs16.x
Environment:
Variables:
EventBusName: !Ref OrderEventsBus
Events:
ProcessorEvent:
Type: EventBridgeRule
Properties:
EventBusName: !Ref OrderEventsBus
Pattern: {"source" : [{ "prefix": "com.majestic.orders" }]}
# this is the shipping confirmation state machine, this simulates shipping and confirmation of shipping for the product
ShippingConfirmationMachine:
Type: AWS::Serverless::StateMachine
Properties:
Definition:
StartAt: TaskState
States:
TaskState:
Type: Task
Resource: arn:aws:states:::lambda:invoke
Parameters:
FunctionName: ${FunctionArn}
Payload.$: $
End: true
Policies:
- AWSXrayWriteOnlyAccess
- Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:CreateLogDelivery
- logs:GetLogDelivery
- logs:UpdateLogDelivery
- logs:DeleteLogDelivery
- logs:ListLogDeliveries
- logs:PutResourcePolicy
- logs:DescribeResourcePolicies
- logs:DescribeLogGroups
Resource: '*'
- LambdaInvokePolicy:
FunctionName: !Ref ShippingFunction
Tracing:
Enabled: true
Type: STANDARD
DefinitionSubstitutions:
FunctionArn: !GetAtt ShippingFunction.Arn
Events:
ShippingEvent:
Type: EventBridgeRule
Properties:
EventBusName: !Ref OrderEventsBus
Pattern: {"source" : [{ "prefix": "com.majestic.orders" }]}
# this is the shipping lambda function which is invoked by the Step Functions state machine
ShippingFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: src/
Handler: shipping.handler
Runtime: nodejs16.x
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 5
# Event Rule for CloudWatch Logs, this time separately in CloudFormation syntax so you know how to set it up this way too
# this one will intercept all events so we can easily debug our app / you can use Events Archives and Replays for this as well
EventRuleToCloudWatch:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
Name: EventRuleToCloudWatch
EventBusName: !Ref OrderEventsBus
EventPattern: {"source" : [{ "prefix": "" }]}
Targets:
-
Arn: !GetAtt CloudWatchLogGroupForEventBridgeOrders.Arn
Id: TargetCloudWatch
# CloudWatch Log Group where we will send all events
CloudWatchLogGroupForEventBridgeOrders:
Type: AWS::Logs::LogGroup
Properties:
LogGroupName: OrdersAPI/Events
RetentionInDays: 14
PermissionPolicyForCloudWatchLogsUsage:
Type: AWS::Logs::ResourcePolicy
Properties:
PolicyName: EventBridgeToCloudWatchLogsPolicy
PolicyDocument: !Sub >
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "EventBridgeToCloudWatchLogsPolicy",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"events.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream"
],
"Resource": [
"${CloudWatchLogGroupForEventBridgeOrders.Arn}"
]
},
{
"Sid": "EventBridgetoCWLogsPutLogEventsPolicy",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"events.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": [
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": [
"${CloudWatchLogGroupForEventBridgeOrders.Arn}"
],
"Condition": {
"ArnEquals": {"AWS:SourceArn": "${EventRuleToCloudWatch.Arn}"}
}
}
]
} For this you will also need 2 lambda functions in the /src folder. You can check the full solution in my github repo if you have no experience implementing the lambdas on your own.
